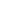Display of application scenarios for some cables

2025-02-21
145
-
Power Cables
-
-
High - Voltage (HV) Power Cables: These are mainly used in power transmission grids. For example, in national - level power grids, 110kV, 220kV, and even higher - voltage power cables are employed to transmit electricity over long distances from power generation sources like power plants to urban and rural substations. In large - scale industrial parks, HV power cables are also crucial for supplying high - capacity power to factories with high - power equipment.
-
-
Low - Voltage (LV) Power Cables: Widely used in residential buildings, commercial complexes, and small - scale industrial facilities. In homes, LV power cables are responsible for distributing electricity from the building's main power supply to various electrical appliances, such as lighting fixtures, air conditioners, and refrigerators. In commercial buildings, they power elevators, escalators, and office equipment.
-
Communication Cables
-
-
Optical Fiber Cables: They are the backbone of modern communication networks. In the field of long - distance telecommunications, optical fiber cables are used to transmit large - volume data, including voice, video, and internet data, across cities, countries, and even continents. For example, submarine optical fiber cables connect different regions around the world, enabling seamless international communication. In local area networks (LANs) of enterprises and data centers, optical fiber cables provide high - speed and stable data transmission for servers and computer networks.
-
-
Twisted - Pair Cables: Commonly used in short - range communication scenarios. Category 5e, Cat6, and Cat7 twisted - pair cables are popular in Ethernet networks within buildings. They are used to connect computers, printers, and other network - enabled devices in offices, schools, and homes, providing a cost - effective solution for local network connections.
-
Control Cables
-
-
These are extensively used in industrial automation systems. In factories, control cables are used to connect programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and actuators. For example, in an automobile manufacturing plant, control cables transfer control signals from the central control system to various robotic arms and conveyor belts, ensuring the smooth operation of the production line. They are also used in power plants to control the operation of turbines, generators, and other equipment.
 2025-02-21
2025-02-21  145
145